Settings
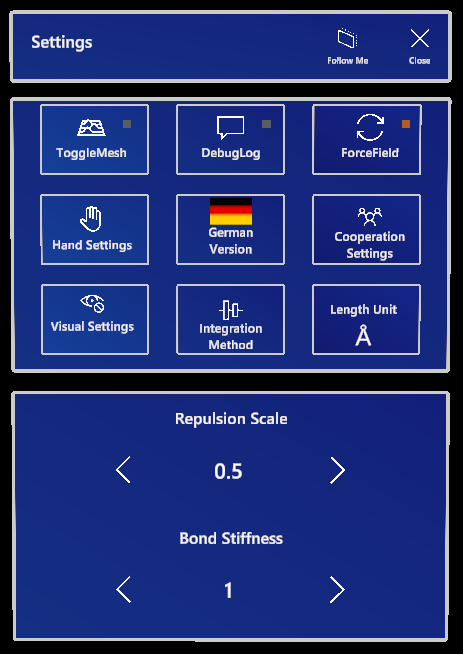
All toggle buttons in the settings are equipped with a colored square indicating whether they are currently set to “on” or “off”.
Toggle Mesh
This button turns the rendering of the spatial awareness of OpenXR on and off. The real world surroundings are detected by your device in a (usually) 2.5 second interval. Toggling the button does not turn on/off the detection of your surroundings, just the rendered wireframe overlay.
Toggle Log
The Debug Log button shows and hides the debug log. Note: changing scenes does not clear the debug log for easier error detection.
Toggle Force Field
chARpack calculates forces in the background to empirically simulate a semi-realistic molecule behavior. The forces are integrated using a simple Midpoint integration by default. The force field is developed to be responsive, lightweight, and makes it easy to handle objects in the chARpack Molecular Builder environment. Toggling the force field off stops any calculations in the background and lets every part of the molecule move unhindered (without any force feedback). This mode comes in handy when creating a bond within a molecule where the force field makes it difficult to bring these two dummies together.
Hand Settings
The Hand Settings button opens (or closes) a submenu containing settings related to the user’s hands.
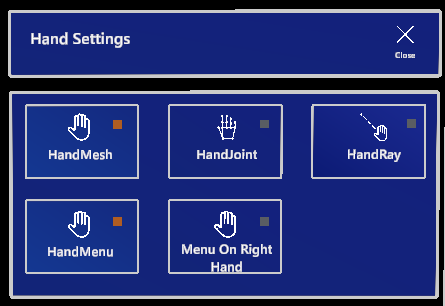
Hand Visual Toggles
The first two buttons change the hand visuals. You can have your hand rendered as a mesh, joint visuals or no rendering of the hand tracking.
Toggle Hand Ray
By default, a dashed ray is rendered from the tip of your index finger in the direction you’re pointing. You can toggle this behaviour on or off.
Toggle Hand Menu
This button enables or disables use of the hand menu. By default, the menu is enabled for user comfort; if you prefer not using it, you can turn it off using this button. However, this will also disable the Fragment Rotation Mode and Measurement Mode button since they are part of the hand menu functionality.
Toggle Menu Handedness
The hand menu is rendered next to a user’s left hand by default (since this is most comfortable for most right-handed people). If you are left-handed or would simply prefer using the hand menu with your left hand, this button changes its positioning so it only shows up next to your right hand.
Switch language
This button switches the application’s language between German and English.
Cooperation settings

In cooperation mode, a box and a ray are rendered around the head of every user to indicate where they are and where they are looking. If you find this behaviour distracting, you can turn each of the functionalities off.
You may also decide whether measurements made on your device should be transmitted to the server via the network; by default, this behaviour is active.
Visual Settings
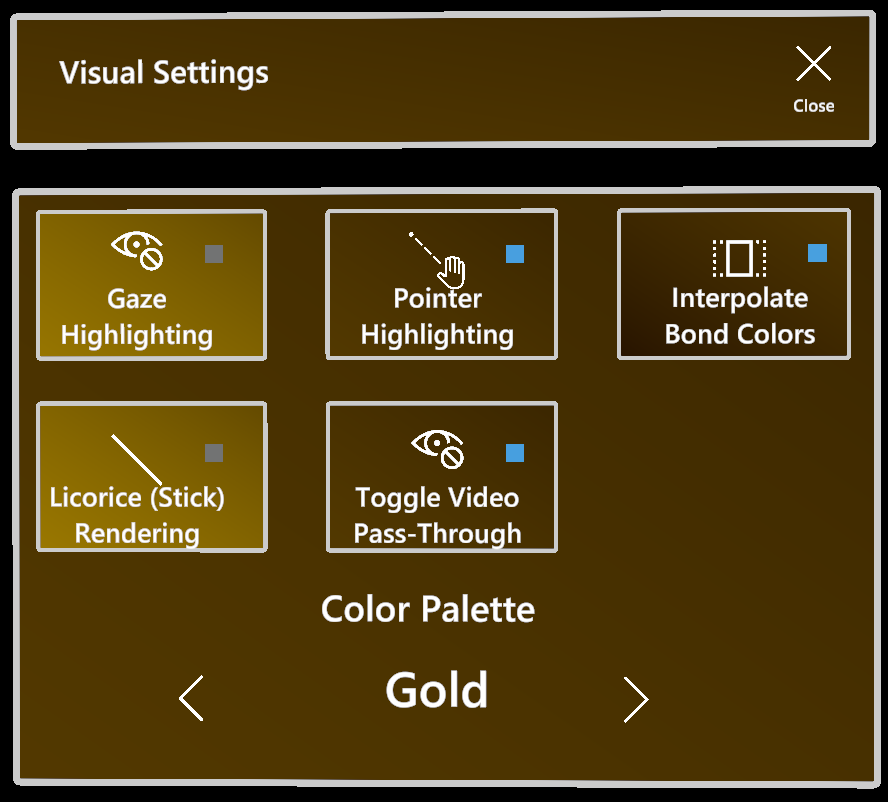
Gaze highlighting
chARpack utilizes the eye tracking capabilities of the device to highlight the atom the user is currently looking at. This behaviour is optional and can be toggled using this button.
Pointer highlighting
As with gaze highlighting, atoms are highlighted when a pointer (a user’s index finger) gets close to it. This behaviour can be useful in cooperation scenarios to point to specific atoms without causing misunderstandings. It can be toggled using this button.
Interpolate bond colors
By default, the color of bonds between atoms is interpolated from the atom’s color to a neutral grey in the middle to provide a smooth look. If you prefer the look of bonds comprised of two solid-colored halves, you can toggle the interpolation off.
Licorice (stick) rendering
By default, atoms are rendered as spheres with relatively thin cylindrical bonds connecting them. This button activates the “licorice” rendering method where the molecule is rendered as a network of comparatively thick sticks (bonds) in the colors of their respective connected atoms.
Video pass-through
This button toggles the optional behaviour of VR devices that pass video footage of their surroundings from their camera to the user. This is useful in cases of live collaboration where every participant would like to see the room they are in, but can be toggled off for remote collaboration purposes.
Color scheme
chARpack support multiple different color schemes that change the background color of menus and the color of the toggle indicators.
Integration method
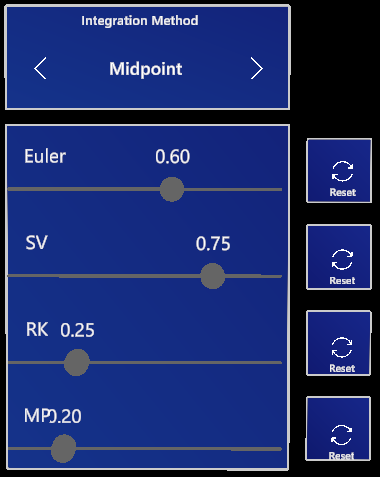
The integration method is the method used for numerical integration in force field computations. You can choose between:
- Midpoint integration (default)
- Euler method
- Verlet method
- Runge-Kutta integration
- Heun method
- Ralston method
- Steepest Descent
The sliders below influence the time factors used for Euler, Verlet, Runge-Kutta and Midpoint integration methods, respectively. Setting any of these time factors to too high a number may cause molecules to become unstable.
Length unit
This button toggles the unit of measurement used in tooltips and on distance measurements between Angstrom and picometers.
Bond Stiffness
The bond stiffness parameter changes the number of force field iterations and therefore the perceived stiffness of the molecule. The number of iterations changes how fast the molecule will go into its minimal state. A lower number makes the molecules feel rubbery, higher numbers will keep the structure intact.
Note: A higher number of iterations means more computational power goes into the force field calculation/iteration. If you experience performance issues, please turn this parameter to 0. This usually happens for scenes with large molecules.
Repulsion scale
The repulsion scale parameter changes the weighting of the Van der Waals radius for the hard sphere potential in force field computations. For a high repulsion scale, atoms easily start to move by the proximity of close atoms. A low repulsion scale may make some changes possible that aren’t with a higher number. However, too low a repulsion scale may cause molecules to get tangled.